Highlights
- Section and member design of aluminium products according to the latest EN 1999-1-1 + A1 + A2: 2013.
- Classification and effective section derivation for any aluminium cross-section shape: whether taken from internal libraries, drawn by the user, or imported from CAD software.
- Effective section derivation for localised buckling effects and heat-affected zones from both longitudinal and transverse welds on the member.
- Clear reporting at different levels of detail: from a brief summary per member to a detailed calculation report with formulas and references to the articles in the code.
Benefits
Proper and precise handling of aluminium members in SCIA Engineeris achieved by:
- considering all localised buckling effects as well as heat-affected zones in effective section calculations and further design verifications;
- on a span level, determination of buckling factors and second-order effects for global member stability.
- fast checking of aluminium structures due to optimised design routines and parallel processing.
- the compatibility of this design functionality with advanced analysis features, such as the various types of nonlinearity, absences, 2D FEM stress analysis of cross-sections, etc.
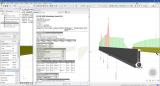

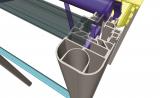
Cross-section analysis
SCIA Engineer has unique, versatile routines for analysis of thin-walled sections: section classification and derivation of effective sections are the essential step before applying the checking rules of the code.
- On top of what is available for steel design, the aluminium cross-section tools also take into account the presence of welds.
- The Profile Library contains a wide variety of shapes that users can adapt, store and use according to their needs;
- By using the General Cross-section Editor (included in module sen.05), users can create any cross-section shape and use it in the analysis and structural design; beside the integrated drawing tools there, cross-sections can be imported from dxf and dwg files;
- SCIA Engineer automatically assigns wall types (internal, fixed, symmetrical or asymmetrical outstands) to the parts of all known cross-section shapes, even when these are combined (welded or bolted) together.
- Reduced cross-section properties are calculated for compression, strong- and weak-axis bending, taking into account local and distortional buckling and the effect of HAZ.
- The obtained effective sections can he displayed graphically, and all iterations of the calculation are reported in tables.
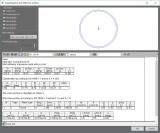
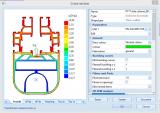
Heat-affected zones
When welding is used as connection measure on aluminium members, localised stability effects may be intensified due to softening of the material. Eurocode 9 puts special attention on the correct handling of welds on the level of design.
In SCIA Engineer, users can input both longitudinal and transverse welds onto the members. Welds will augment the used effective section properties in their heat-affected zone (HAZ). Transverse welds will results in a completely new effective section along the extent of the HAZ.
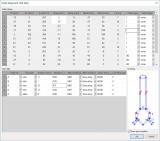
Checks
Since version 19.1, checks are performed according to the latest EN 1999-1-1:2007 + A1:2010 + A2:2013 with special considerations for transverse welds.
- Section checks are performed for axial forces, bending moments, shear forces, torsion, warping, and the combination of these load effects (N + My,z + Vy,z, Vy,z + T).
- Stability checks are performed for flexural buckling, torsional and torsional-flexural buckling, lateral torsional buckling, shear buckling for I-sections (symmetrical or asymmetrical), combined bending and axial compression.
- An automatic design (AutoDesign) functionality makes it possible to optimize the dimensions of library or parametric cross-section in order to obtain optimal utilisation.
- Arbitrary cross-sections (with haunches, variable height) and members with holes can also be designed.
- The program also allows for the "most dangerous" load combination keys to be extracted and used further for e.g., stability or second-order analysis. Most dangerous here refers to the load combinations that result in the highest section or stability utilisation for all or selected aluminium members.


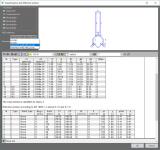
Reporting
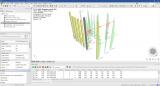
The Aluminium design module benefits from an interactive reporting interface, where the results of the design are easily accessible in various forms:
- colour-coding utilisation diagrams in the 3D scene helps to quickly identify problems anywhere in the structure;
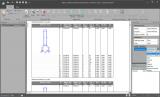
- the design outcome for all members is easily printable in table form via the Brief report or via Table Results;
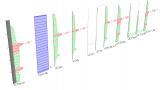
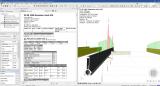
- a Summary report per member summarised all important parameters of the design and all checks on a single page;
- a Detailed report shows all calculations as formulas (or tables, if the user prefers) with references to the used articles in the code, letting the user follow and verify the logic and steps of the design;


- the Summary and Detailed report are directly accessible by double clicking on the rows of Table Results. In this way, the user quickly makes the connection between details of the calculation and the members visualised on the screen.
- Errors, warnings and notes can be shown interactively by hovering on specific members in the 3D scene.
- A detailed overview of the section classification and effective section derivations can be added to the Engineering report as well.
- at all times when plotting results, the selected settings (e.g., selected load combination, member names, type of calculation and extremes) are displayed via the Result Legend in the top left corner;
- besides the overall utilisation, the user can plot specific checks onto the members using the Result Components.
First introduced in version 19.1

Want to try SCIA Engineer yourself?
Explore how our software and services can help you optimise your work and boost your productivity. Try it for yourself with a free 30-day software trial.
Download a free 30-days full trial