Vibration analysis
The new SCIA Engineer vibration analysis module allows engineers to apply nodal, line and surface harmonic loads. The harmonic loads can be both in-phase and out-of-phase.
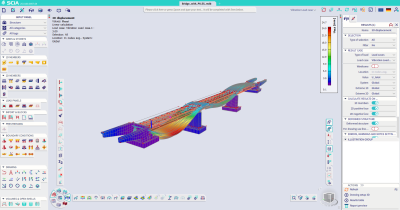
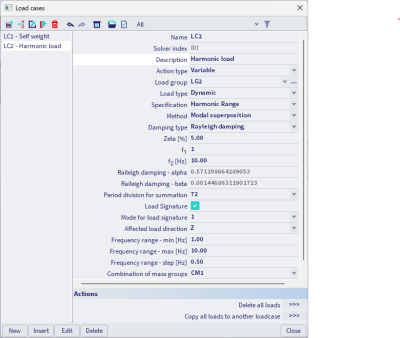
The computation can be performed for a single frequency of interest or a range of frequencies. Either a constant or Rayleigh’s damping can be applied.
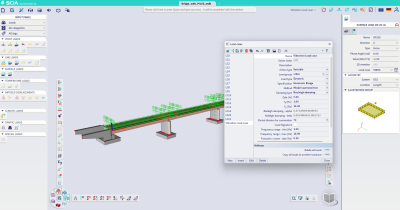
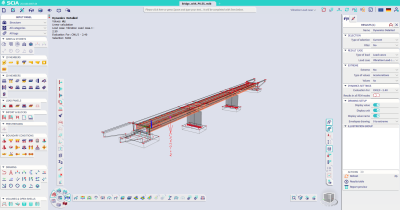
Furthermore, the sign of the harmonic load can be assigned according to a specific modal shape, in order to quickly reproduce the worst-case-scenario loading configuration as specified in several design guidelines for buildings and bridges (for instance, SETRA [Service d'études techniques des routes et autoroutes] design guide for footbridges).
Additional results such as acceleration, velocity and displacement are available in the newly introduced “Dynamic Detailed results” menu, both as peak and RMS values.
Design and check in construction stages
Design and checks of members can now be performed with internal forces for individual stages of construction. This option is available for most of the available materials. It is possible to choose a specific construction stage or select all stages.
It is important to note the following limitation: The buckling systems cannot account for absent elements in stages, even when executing a check for a construction stage. It is not yet possible to define different buckling settings per stage.
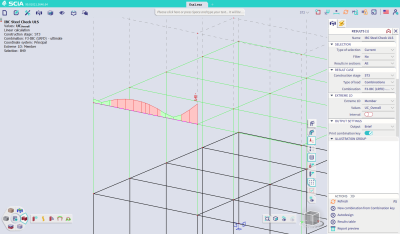
Supported items include:
- Non-prestressed concrete:
- Staged results are supported for 1D and 2D checks
- Supported for both EC-EN and SIA, but not for ACI and NBR codes
- Phased cross-sections are not supported
- Code dependent deflections are not supported
- Prestressed concrete:
- All EC-EN checks are supported
- Phased cross-sections are supported
- Fibre reinforced concrete:
- All EC-EN checks are supported
- Steel
- EC-EN, SIA and AISC codes are supported, NBR is not supported
- Phased cross-sections are not supported at the moment
- Connection design and scaffolding couplers are not supported
- Aluminium EC-EN design is supported, but not for phased cross-sections
- Cross-laminated timber design is supported
More details on this topic can be found in the online help at help.scia.net.
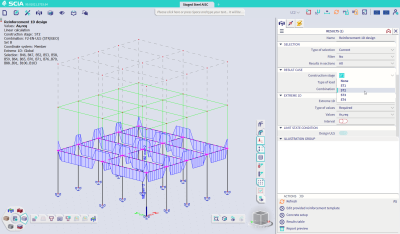
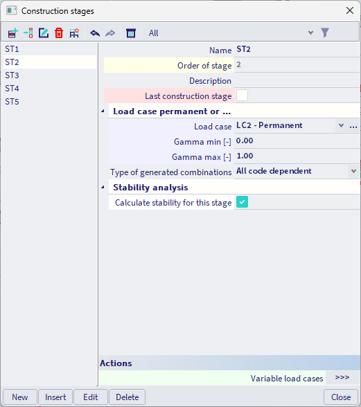
Stability analysis in construction stages
Following the new functionalities introduced in the previous version, SCIA Engineer 25 now allows the engineers to perform a stability analysis in individual stages of construction. This facilitates the workflow especially when designing multistorey buildings and bridges.
3D wind load generator
The 3D wind load generator has been extended with an improved handling of corner zones for roofs, friction forces and wind generation for canopy roofs with a force coefficient approach.
As specified in EN1991 1-4 Chapter 5, the forces generated by wind friction can also be considered in the calculation.
Wind load on canopy roofs can be applied through pressure coefficient (Cp) approach or through force coefficient (Cf) approach, as specified by the Eurocode.
The 3D wind load generator is available with all its functionalities for EN 1991-1-4:2005. The 3D wind load generator is also available for ASCE 7-05 but it supports only closed structures without awnings and friction load.
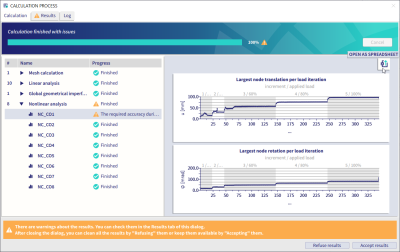
Convergence graph for nonlinear analysis
The convergence graphs for nonlinear calculations are reintroduced in SCIA Engineer 25 in a new and improved form. A graph for each nonlinear combination can be displayed both during and after the calculation by clicking on the combination you are interested in. Both a graph for the highest displacement and rotation in the last 500 iterations are shown. When you hover the mouse over any node, the related values pop up.
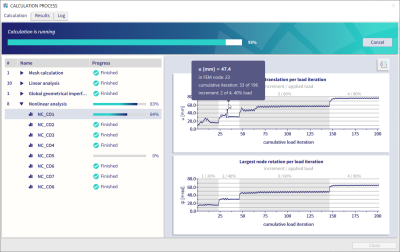
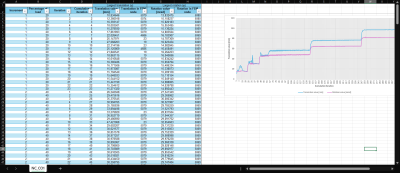
In order to see the full detail of all the values and all the iterations, you can click the top right button to open a spreadsheet where you can analyse every single value or create a bespoke graph in your preferred style.
Bridge combinations improvement
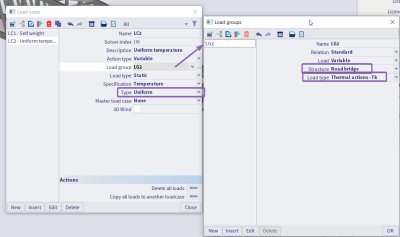
Eurocode combinations for bridges have been extended to account for temperature loads. In the temperature load cases that are part of a temperature load group of a bridge type, the user can now define whether this load case is describing a uniform or gradient temperature.
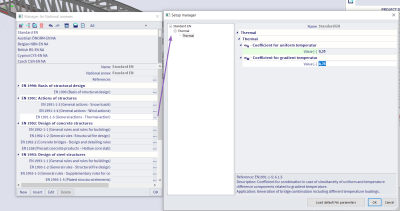
The uniform and gradient temperature is then combined with the coefficients as described by the rules in EN 1991-1-5 for temperature loading. The user can optionally adapt these coefficients in the national annex setup.
Update of AISC and ASCE code
Update of the combination rules to ASCE 7-22
In SCIA Engineer 25 the rules for load combinations according to the American codes have been updated to the latest rules described in ASCE 7-22. When opening an old project in version 25, any present American code combinations are automatically updated to the latest rules. The user is notified by a message that the code combinations have been adapted.

Update of the steel design to AISC 360-22
A similar update has been made for the steel design, where all checks are now executed according to the latest AISC 360-22 rules.
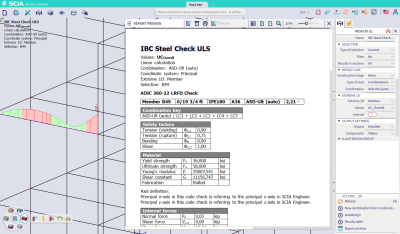
All references both inside the software and in the output have been adapted, and the user can find all the theoretical background on the used rules in the online help.
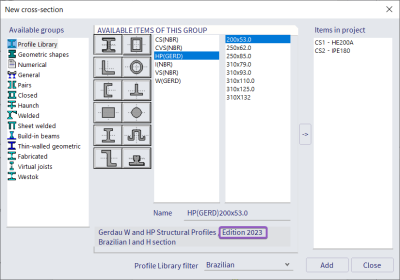
Update of the American and Brazilian profile libraries
Three updates and additions have been made to the SCIA Engineer profile library:
1. Update of the American profiles
2. Update of the Brazilian profiles
3. Additional configuration for L pair sections

Link with FRILO B5+
With SCIA Version 25 and Frilo R2025-1, another interface between SCIA Engineer and FRILO is released. It is possible to transfer a reference column from a 3D model in SEN to the reinforced concrete column programme B5+ from FRILO. The great benefit is that all internal forces are automatically transferred to the Frilo column application in the form of external loads. Furthermore, the component-based calculation approach makes the results easy to understand. In addition, users can choose between different calculation modes - design, verification, ultimate load - or, for example, take high-strength steel into account. B5+ covers all the design checks required by EC2 - both ULS and SLS - in a single run and a concise design report. Even under fire conditions, if required.
How it works:
- In the SCIA Engineer model find the column you want to design/check in the FRILO application.
- Once you have decided which column you want to design, select one single column and start the FRILO Reinforced Column command (via SCIA Spotlight or Menu bar > Design > External tools > FRILO Reinforced Column).
- After you call this command, FRILO Reinforced Column B5+ application should now launch and the stripped structure is exported.
The UI is translated into:
- German
- English
- Polish

Help documentation: https://help.scia.net/25.0/en/#data_transfer/frilo_b5+/frilo_reinforced_concrete_column_b5+.htm

Want to try SCIA Engineer yourself?
Explore how our software and services can help you optimise your work and boost your productivity. Try it for yourself with a free 30-day software trial.
Download a free 30-days full trial